Medical Uses of Cannabidiol:
- CBD is a phytocannabinoid discovered in 1940 and is one of 113 identified cannabinoids in cannabis plants.
- CBD accounts for up to 40% of the plant’s extract.
- Clinical research on CBD includes studies on anxiety, addiction, psychosis, movement disorders, and pain.
- CBD is sold as a herbal dietary supplement with unproven therapeutic claims.
- Limited evidence exists for neurological effects of cannabidiol in humans.
Epilepsy Treatment:
- FDA approves Epidiolex for seizures associated with specific syndromes.
- Epidiolex is generally well tolerated but may cause minor adverse effects.
- Studies have shown Epidiolex to be effective for epilepsy treatment.
- In the EU, Epidyolex is indicated for use in conjunction with clobazam.
- Epidiolex is the first plant-derived cannabidiol approved in the US and Europe.
Research and Regulation:
- Federal illegality in the US has hindered CBD research.
- Research on other neurological disorders is inconclusive.
- FDA advisory warns about unknown effects of CBD during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Studies have shown Epidiolex to be effective for epilepsy treatment.
- CBD products need safety tests and authorization for legal commerce in Europe.
Non-Intoxicating Effects and Side Effects:
- CBD does not cause intoxication like THC.
- Common side effects of CBD include tiredness, sedation, diarrhea, and changes in appetite.
- Reports of CBD-induced illnesses to poison control centers have increased.
- CBD may reduce adverse effects of THC at high doses.
- CBD interacts with neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and GABA.
Legal Status and Cultural Impact:
- CBD became legal for recreational and medical use in Canada in October 2018.
- Cannabidiol has been used by athletes worldwide, with WADA removing it from the banned substances list.
- FDA issued warning letters for false advertising and illegal marketing of CBD.
- Hemp cultivation for CBD production is subject to specific rules and regulations.
- CBD products are not eligible for legal commerce in Europe until at least 2021.
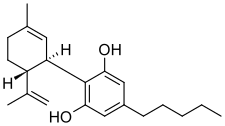
Cannabidiol (CBD) (/kæ.nə.bə.ˈdaɪ.əl/) is a phytocannabinoid discovered in 1940. It is one of 113 identified cannabinoids in cannabis plants, along with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and accounts for up to 40% of the plant's extract. As of 2022[update], clinical research on CBD included studies related to the treatment of anxiety, addiction, psychosis, movement disorders, and pain, but there is insufficient high-quality evidence that cannabidiol is effective for these conditions. CBD is also sold as a herbal dietary supplement promoted with unproven claims of particular therapeutic effects.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Epidiolex, Epidyolex |
| Other names | CBD, cannabidiolum, (−)-cannabidiol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a618051 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Addiction liability | Low |
| Routes of administration | Inhalation (smoking, vaping), buccal (aerosol spray), oral (solution) |
| Drug class | cannabinoid |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability |
|
| Elimination half-life | 18–32 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.215.986 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H30O2 |
| Molar mass | 314.469 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 66 °C (151 °F) |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Cannabidiol can be taken internally in multiple ways, including by inhaling cannabis smoke or vapor, oral, and as an aerosol spray into the cheek. It may be supplied as CBD oil containing only CBD as the active ingredient (excluding THC or terpenes), CBD-dominant hemp extract oil, capsules, dried cannabis, or prescription liquid solution. CBD does not have the same psychoactivity as THC, and can modulate the psychoactive effects of THC on the body if both are present. CBD heated to 250–300 °C may partially be converted into THC.
In the United States, the cannabidiol drug Epidiolex was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2018 for the treatment of two epilepsy disorders. While the 2018 United States Farm Bill removed hemp and hemp extracts (including CBD) from the Controlled Substances Act, the marketing and sale of CBD formulations for medical use or as an ingredient in dietary supplements or manufactured foods remains illegal under FDA regulation, as of 2024[update].





