**Species and Cultivars**:
– Genus Actinidia comprises around 60 species.
– Commonly sold kiwifruit species include A. deliciosa (fuzzy kiwifruit), A. chinensis, A. arguta, A. kolomikta, A. melanandra, A. polygama, and A. purpurea.
– Notable cultivars include Hayward (A. deliciosa), Saanichton 12, Blake, Hort16A, Gold3 (A. chinensis), and Issai (hybrid of A. arguta, A. kolomikta, A. polygama).
**Cultivation and Pollination**:
– Kiwifruit can be grown in most temperate climates, with different species used as substitutes where needed.
– Commercial farming involves different breeds for rootstock, fruit-bearing plants, and pollinators.
– Kiwifruit plants are generally dioecious, with male and female plants, requiring pollination for fruiting.
– Some varieties can self-pollinate, but cross-pollination with male plants is beneficial for better yields.
**Maturation, Harvest, and Storage**:
– Kiwifruit is hand-picked and grown on support structures due to high yields.
– Vigorous pruning is necessary, with fruit borne on one-year-old and older canes.
– Production peaks at 8-10 years old, with variable seasonal yields.
– Kiwifruit ripens at different times in the northern and southern hemispheres.
– Proper storage methods can extend the shelf life of ripe kiwifruit.
**Pests, Diseases, and Production**:
– Pseudomonas syringae actinidiae (PSA) is a bacterial strain affecting kiwifruit, with new resistant varieties developed.
– Global kiwifruit production in 2020 was 4 million tonnes, with China as the leading producer.
– Kiwifruit exports from New Zealand surpassed domestic consumption by 1976.
– Italy and New Zealand are significant kiwifruit producers, with Italy adapting grape production techniques.
– Kiwifruit production expanded globally outside New Zealand in the 1980s.
**Nutrition, Culinary Uses, and Cultural Significance**:
– Kiwifruit is low in calories, high in fiber, and rich in essential nutrients like Vitamin C and potassium.
– Kiwifruit can be eaten raw, juiced, used in baked goods, and as a meat tenderizer due to actinidain content.
– Kiwifruit seed oil contains omega-3 fatty acids, and the pulp contains carotenoids beneficial for health.
– Traditionally in China, kiwifruit was used medicinally, and it has cultural significance in aiding growth and post-childbirth recovery.
– Kiwifruit allergy, recognized in clinical studies, can range from mild symptoms to severe anaphylaxis, with actinidain being a common allergen.
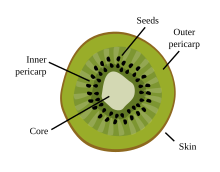
Kiwifruit (often shortened to kiwi outside New Zealand and Australia) or Chinese gooseberry is the edible berry of several species of woody vines in the genus Actinidia. The most common cultivar group of kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa 'Hayward') is oval, about the size of a large hen's egg: 5–8 centimetres (2–3 inches) in length and 4.5–5.5 cm (1+3⁄4–2+1⁄4 in) in diameter. It has a thin, fuzzy, fibrous, tart but edible light brown skin and light green or golden flesh with rows of tiny, black, edible seeds. The fruit has a soft texture with a sweet and unique flavour.

A = A. arguta, C = A. chinensis, D = A. deliciosa, E = A. eriantha, I = A. indochinensis, P = A. polygama, S = A. setosa.


Kiwifruit is native to central and eastern China. The first recorded description of the kiwifruit dates to the 12th century during the Song dynasty. In the early 20th century, cultivation of kiwifruit spread from China to New Zealand, where the first commercial plantings occurred. The fruit became popular with British and American servicemen stationed in New Zealand during World War II, and later became commonly exported, first to Great Britain and then to California in the 1960s.





